Table of Contents
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computing and storage resources without active management of those by the user. It is like the renting of these resources and paying for only those.
In the traditional setup, you need to manage the servers, networks, switches, routers and desktop or laptop machines, however, in the Cloud setup you just need an internet connection and a cloud provider to start with.

Advantages of Cloud Computing
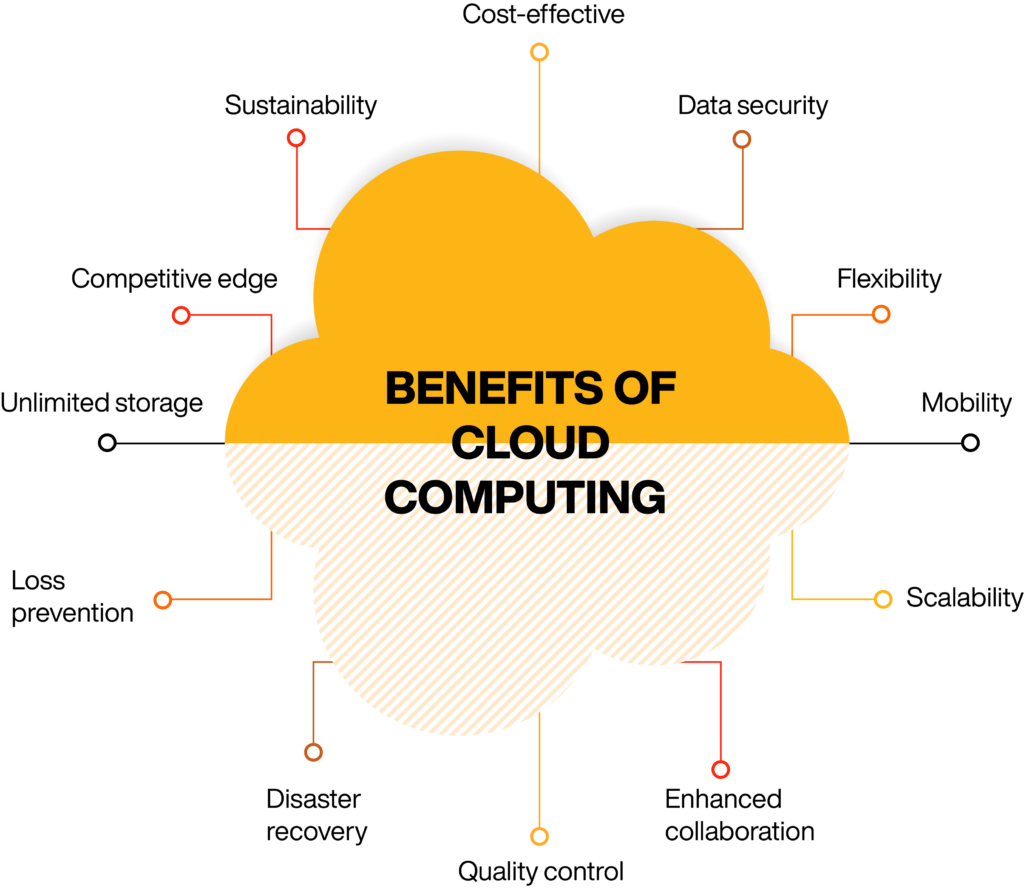
Below are some of the advantages of moving to cloud from traditional system setups:
Cost-effective
Cloud computing is a pay-as-you-go model and involves no upfront cost. Also, when you do not need any resources, you can stop paying for them.
Scalability & Elasticity
You can increase or decrease the resources as per demand.
Current & Updated
While using cloud resources you can ensure that the resources are updated by the Cloud Provider on a frequent basis, and you are using the current and latest versions of the resources.
Reliable
All the resources in the Cloud provide fault-tolerance and disaster-recovery mechanisms.
Global
Cloud datacentres are spread across the world and they provide the best response times anywhere in the world for their customers.
Secure
The cloud datacentres are heavily guarded with walls, security cameras, and digital security and they provide a high level of security to their users.
Terminologies in Cloud Computing
Below are some of the terminologies used in cloud computing:
Economies of Scale
Economies of Scale: It is the ability to acquire storage and computing resources on a large scale at a cheap price and then pass these resources to the customers at a discounted price.
CapEX and OpEx
CapEx and OpEx: CapEx is the Captial Expenditure that is the upfront or the initial investment required for setup whose value decreases over time. Eg: Routers, switches etc. OpEx is the Operational Expenditure which is the cost that you pay as you utilize the resources like manpower, electricity and so on. With Cloud model, both CapEx and OpEx are reduced drastically.
Vertical and Horizontal Scaling
Vertical and Horizontal scaling: The cloud model provides both vertical scaling (adding more resources like RAM, memory to existing resources) and horizontal scaling ( adding more servers to an existing set of servers).

Type of models
Now let us come to the types of cloud models. There are three types of it:
Public cloud
Owned by Cloud Providers, this type of model has shared resources and provides those to multiple organizations. These resources are available to anyone over the Internet. No in-depth technical knowledge is required to set up or manage or use these resources.
Private cloud
Owned and operated by organizations, this cloud model has its own cloud environment. This type of model is required when the organization has data that it cannot share outside. E.g.: Medical data that cannot be updated publicly. Deep technical knowledge because you need to create, deploy, and maintain the cloud environment.
Hybrid cloud
This is the combination of public and private cloud models. When the organization contains data that cannot be stored outside, it is stored in the private cloud and the rest can be stored in the public cloud. You need highly skilled labour to maintain and deploy the cloud within the organization.
Cloud Service Delivery Models
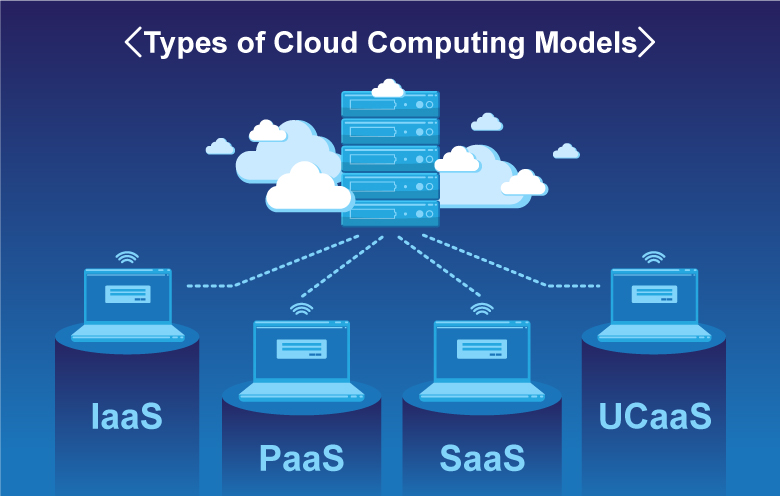
Cloud providers deliver three types of services to its users:
IaaS:
It stands for Infrastructure as a Service and it offers Hardware as a service. This hardware is hosted by cloud providers in their datacentres. With an internet and subscription to cloud customers can use rack, switches and firewalls provided by the cloud providers.
PaaS:
It stands for Platform as a Service and it offers developers an environment so that they can develop applications as fast as possible without worrying about underlying infrastructure. E.g.: DBMS, Docker, Kubernetes hosted by the cloud providers.
SaaS:
It stands for Software as a Service and it offers software hosted by the cloud providers. E.g.: Office 365, Facebook, Gmail, and Salesforce.
Some examples of cloud providers are Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).

Leave a Reply