Table of Contents
What is UNIX?
Unix is a multiuser operating system developed by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie in 1970 at AT&T bell lab. Unix is proprietary software. Meanwhile, no one can duplicate this operating system because the source code is reserved for the company. Unix is rigid with hardware and mainly used for server-based machines. Unix has a high cost and capacity with limited versions because only companies can build new versions.
Versions of Unix Based Operating Systems: BSD, Iris, HP-UX, AIS
What is Linux?
Linux is the most popular operating system. Linux is open source operating system why which is very secure to use and we didn’t need any anti-virus for Linux as compared to Windows. Linux was delivered on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds.
What is the Difference between Unix and Linux?
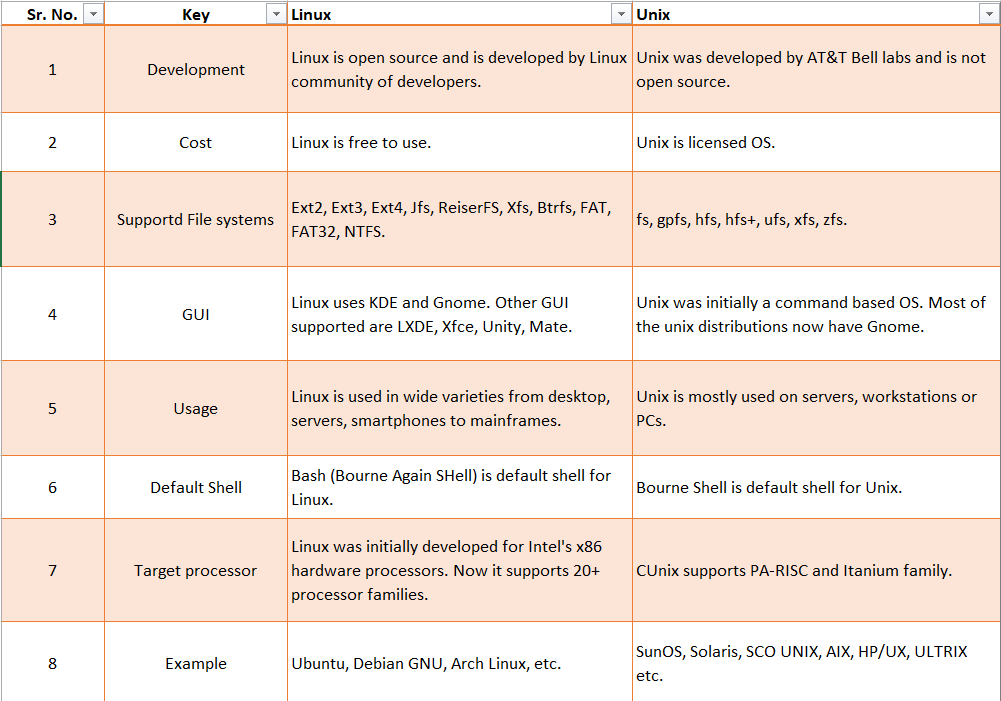
Basic commands of Unix and Linux that everyone should know
| ls | Lists file in a directory |
| rm | Deletes files in a directory |
| mv | Move a file to a different location |
| cat | Display the content of the file |
| rmdir | Remove a directory or subdirectory |
| sudo | Short for ‘super user do‘ sudo is the most popular command |
| mkdir | Create a directory or subdirectory |
| pwd | Show the name of the current directory |
| telnet | Connect to a remote computer |
| who | Display users that are logged on |
| echo | Used to display text or string and mostly used in bash or script files. |
| sed | Perform lots of functions on file like searching, find and replace, insertion or deletion. |
Let’s go deeper into each command:
Is
Is a command used for displaying directory lists in alphabetical order? When you type Is without any parameters it will show your default directory.
Example: ls
Result – Displaying you a list of working directories in alphabetical order.
Example: ls -l
Result – It will display you a ‘long listing’ of files in your directory like file names, long lists of protection information, numbers of characters in the file, and the date and time of the last change to the file.
Example: ls -a
Result – cause all your files will be listed including hidden files and currently working files.
rm
rm command used for deleting specific files that have been entered by space with the file name.
Example: rm newfiles
Result – deletes the file named “newfiles”.
Example: rm newfile oldfile
Result – deletes two files named “newfile”, ”oldfile”.
Example: rm new*
Result – deletes all files that content prefix new.
mv
mv commands can change one or more file names.
Example: mv oldfile newfile
Result – Changes the name of the document “oldfile” to “newfile.” Just a single record will exist.
Example: mv oldfile canister/newfile
Result – Changes the name of the document “oldfile” to “newfile” and places it in the registry/container. Just a single record will exist.
cat
cat command will display the content of the files.
Example: cat newfile
Result – displaying the contents of ‘newfile’ in your terminal.
Example: cat newfile oldfile
Result – now it will display two file’s content – “newfile”, “oldfile” as one continuous display.
Concatenating (combining) files and putting them into another file can also be done with the cat command. The contents of the previous file are permanently lost when files are concatenated with one another.
Example: cat fileone filetwo filethree >newfile
Result – Now it will link together three files – “fileone” , ”filetwo” , ”filethree” into a new file called “newfile”. The original file hasn’t changed.
rmdir
rmdir commands are for removing empty directories on various operating systems.
Example: rmdir mydir
Result – Remove the directory mydir, if it’s empty.
Example: rmdir dir1 dir2 dir3
Result – Remove the directory “dir1, dir2, dir3”, if it’s empty, if it’s not empty an error will be printed for that directory, and the other will be removed.
sudo
There are some commands that need elevated rights to run on a Linux system. It would be best if you ran these as a System Administrator. The su command changes the shell so that it is used as a super user. Until you use the exit command, you can continue to be the super-user.
You can also add an option, such as:
Example: Sudo -k
Result – reset-timestamp invalidates the timestamp file.
Example: Sudo -g
Result – group=group runs commands as a specified group name or ID.
Example: Sudo -h
Result – host=host runs commands on the host.
mkdir
mkdir commands are used to create a new directory file in working files. These commands can create multiple directories at once as well as the permissions of the directories.
Example: mkdir newfile
Result – Create a new file which name is “newfile”
Example: mkdir ~/myfiles
Result – Create a home directory in your home directory, specified here “tilde” (~) to represent your home directory.
pwd
Pwd command will print the full path name of the current working directory to the understood output. All directories are separated by / (Slash).
Example: pwd
Result – Print the name of the working directory. If any of the subdirectories in the path are symbolic links, and you used the symlink names when changing to the directory, the symlink names are printed. Example output:- /home/hope/mysymlink/mydir
Example: pwd -p
Result – Print the name of the working directory using the actual name of the directory, even if any symlink names were used when changing to the directory. For example :- /home/hope/actual_directory_name/actual_subdirectory/mydir
who
who commands without any argument display the system information like user name, logging time, the terminal of the user, and also the hostname of the system.
Example: Who
Result – Display the name of the user that logged on, the line number of the terminal, the time at which the user logged in to the system, hostname of the user who logged in.
echo
“Echo” is one of more highest commands of Linux used to show text or string and for the most part utilized in bash or script files. It helps to portray natural variables present in the framework. The syntax of the “echo” command is given beneath:
Example: echo “Introducing echo”
Result – It will print text that is given into it (Introducing echo).
echo “text” >> [filename] Using this syntax we can move the text into a file
Example: echo “Important data” >> information.txt
Result – It will import text(Important data) into a file name information.txt.
Sed
SED command in UNIX represents stream editor and it can perform heaps of capabilities on files like looking, finding, and replacing addition, or erasure. However, the most well-known utilization of the SED command in UNIX is for a replacement or for finding and supplanting. By utilizing SED you can alter files even without opening them, which is a much speedier method for finding and supplanting something in a file, than first opening that file in VI Editor and afterward evolving it.
Example: sed ‘s/Unix/Linux/’ skilltectfile.txt
Result – Replacing or substituting string: Sed command is generally used to Replace the text in a file. sed command replaces the word “Unix” with “Linux” in the file(skilltectfile.txt).
What We Get From This Blog
Topics we learned in this blog are “Getting Started With Linux And Unix Basic Commands”, “What is the difference between Linux and Unix?” and “Basic commands of Unix and Linux that everyone should know ”.


Leave a Reply